728x90
반응형
경희대학교 김정욱 교수님의 컴퓨터구조 강의를 기반으로 정리한 글입니다.
Misses in Direct-Mapped Cache
Example - 0, 8, 0, 6, 8


Associative Cache Memory
Fully associative cache
- main memory의 block은 cache의 어느 location이든 위치할 수 있음 → cache에 대한 전수탐색 필요
- cache의 모든 위치에 대해 comparator가 병렬적으로 연산 수행 → hardware cost 매우 증가

Set associative cache
- 고정식 숫자의 장소에 main memory block 위치시키는 방법
N-way set-associative cache
- N개의 block을 하나의 set으로 묶는 방법
- set 개수 = 캐시의 전체 블록 개수 / 자유도
- set number = (Block number) modulo (Number of sets in the cache)
- 교체는 least recently used(LRU) block within the set을 기반으로 결정


Associativity(자유도)가 커지면
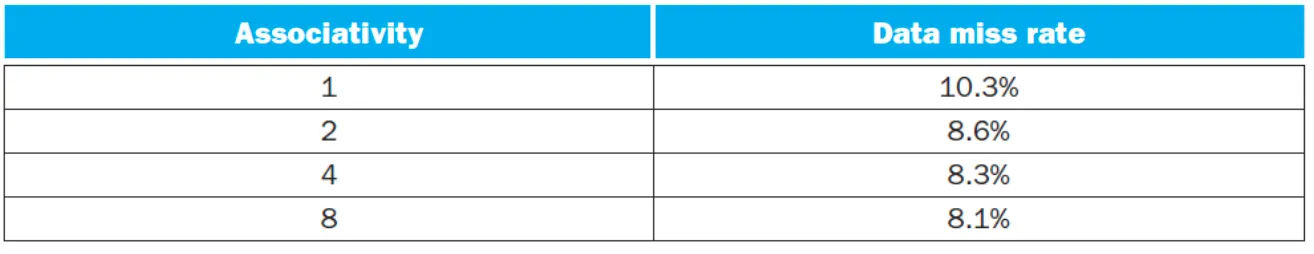
- 장점: miss rate 감소
- 단점: hit time 증가
Misses in associative cache - 0, 8, 0, 6, 8
Fully associative cache

2-way set associative cache

Locating a Block in the Cache
- 4-way set associate cache: 4개의 comparator와 4-to-1 MUX 필요

Choosing Which Block to Replace
Fully associative cache
- 모든 block이 교체 후보
Set-associative cache
- 선택된 set에 포함된 block 중 선택
- Least Recently Used(LRU) → 가장 오래 사용되지 않은 block이 교체됨
Direct-mapped cache
- 요청된 block이 저장될 위치의 block이 교체됨
Size of Tags vs. Tag associativity
- Q. Given 4096 block cache, 4-word block size, and 32-bit address, find the total number of sets and the total number of tag bits for caches that are (1) direct mapped, (2) two-way and (3) four-way set associative, and (4) fully associative
Direct-mapped cache
- 4-word block(2 bits), Offset(2 bits), 4096 blocks(12 bits)
- Total number of sets: 4096(12 bits)
- Total number of tag bits for caches: (32 - 2 - 2 - 12) * 4096 = 66K tag bits
Two-way set associative cache
- Total number of sets: 2048(11 bits)
- Total number of tag bits for caches: (28 - 11) * 2 * 2048 = 34 * 2048 = 70K tag bits
Four-way set associative cache
- Total number of sets: 1024(10 bits)
- Total number of tag bits for caches: (28 - 10) * 4 * 1024 = 72 * 1024 = 74K tag bits
Fully associative cache
- Total number of sets: 1(1 bit)
- Total number of tag bits for caches: 28 * 4096 * 1 = 115K tag bits
Multilevel Caches
- 대부분의 CPU는 추가적 단계의 caching 사용
- primary cache → second level cache 접근 시간 <<< main memory 접근 시간
- primary, secondary cache 모두에 원하는 데이터 없으면 더 큰 miss penalty 발생
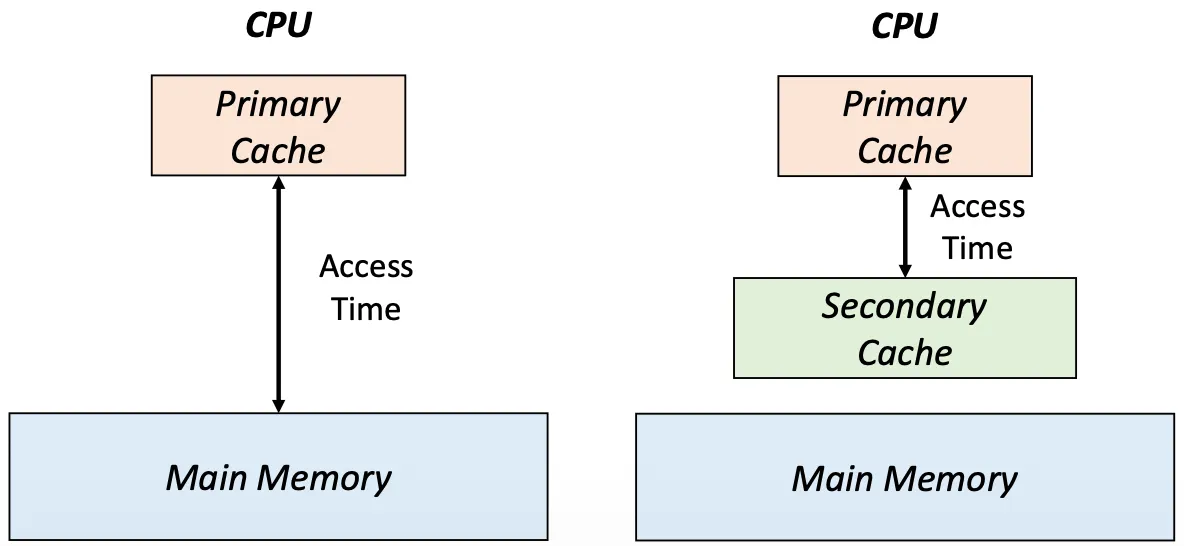
Performance of Multilevel cache
- Processor with a base CPI: 1.0(primary cache로의 참조가 모두 hit일 경우)
- Clock rate: 4 GHz (0.25 ns/clock cycle)
- Miss rate per instruction: 2%
- Main memory access time: 100 ns(including all the miss handling)
- A secondary cache access time: 5 ns
Miss penalty to main memory

Miss penalty to secondary memory

secondary memory를 추가하면 프로세서가 얼마나 더 빨라지는가?(miss rate to main memory 0.5%)
Effective CPI
Only primary cache
- Total CPI = Base CPI + Memory-stall cycles per instruction = 1 + 400 * 2% = 9
With secondary cache
- Total CPI = Base CPI + Memory-stall cycles per instruction(Primary + Second) = 1 + 20 * 2% + 400 * 0.5% = 3.4
- 약 2.6배 더 빠름
Virtual Memory
- 메인 메모리를 Hard disk의 cache로서 사용하는 기법
- CPU, OS에 의해서 관리됨
- 메인 메모리의 용량을 증가시키는 목적
- CPU에서 main memory에 모든 정보가 있다고 생각하게 만드는 기술 → 추가적인 정보는 hard disk에 있음
- 실제 메모리가 아니라 기법
Cache memory vs. Virtual Memory
- Cache memory: CPU의 접근 속도를 높이기 위한 용도
- Virtual memory: main memory의 용량을 늘리기 위한 용도
| Virtual Memory | Cache Memory |
| main memory의 용량 증가 | CPU 접근 속도 향상 |
| technique | memory unit |
| Cache보다 큰 용량 | Virtual보다 작은 용량 |
| main memory의 크기보다 큰 프로그램 실행 | 최근에 사용된 데이터 복사 |
프로그램들은 main memory 공유 가능
- Virtual address: virtual memory의 주소
- Physical address: main memory의 주소
- virtual address는 physical address로 매핑됨 → CPU와 OS가 수행

Address translation(=Address mapping)
- CPU와 OS가 virtual address를 physical address로 변환
- page: Virtual memory가 가져오는 최소 데이터 단위
- page fault: Virtual memory로 physical address에 값이 없을 때 발생
- 다른 virtual address가 같은 physical address를 공유할 수 있음 → 여러 프로그램이 데이터를 공유하기 위해

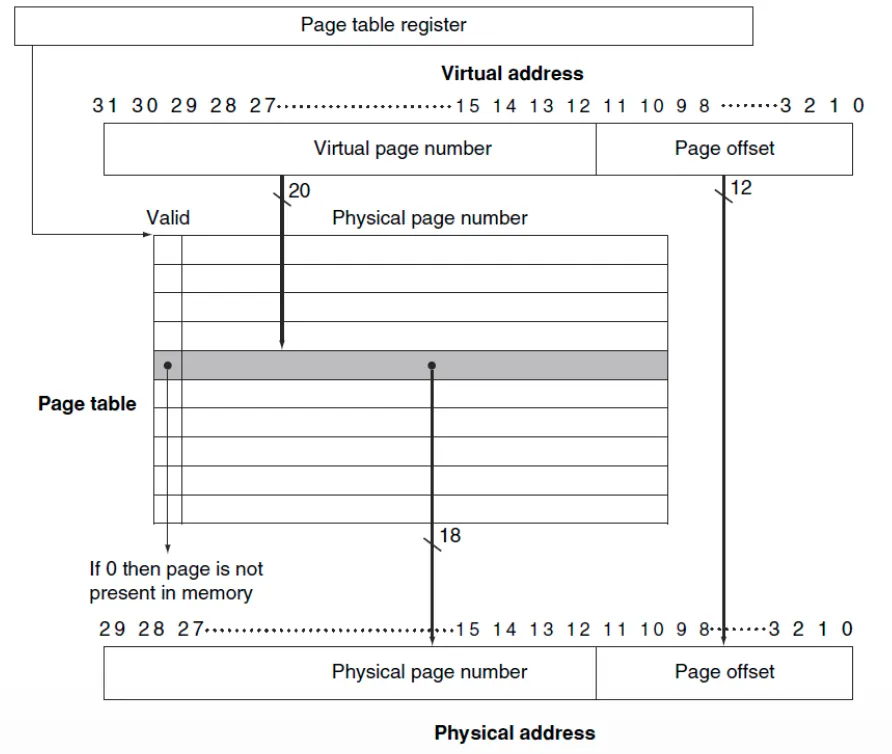
- Virtual Memory: 32bits(2^32 = 4GB)
- Physical Memory: 30bits(2^30 = 1GB)
- Page size: 2^12 = 4096 = 4KB
- 20 bits virtual pages를 18 bits physical pages로 바꿔줌

Translation using Page Table
Page Table
- main memory에 저장됨
- 프로그램마다 각자의 page table이 존재
- Page table register: physical memory의 page table의 주소를 가리킴
Page가 메모리에 존재하면
- Page table: physical page number + other status bits(valid, dirty bits, …) 저장
Page가 메모리에 존재하지 않으면
- OS: page를 disk에서 가져오고(fetch), page table을 갱신(update)
- Page table: swap space의 위치를 참조할 수 있음
- Swap space: virtual memory를 위해 disk에서 제공하는 공간
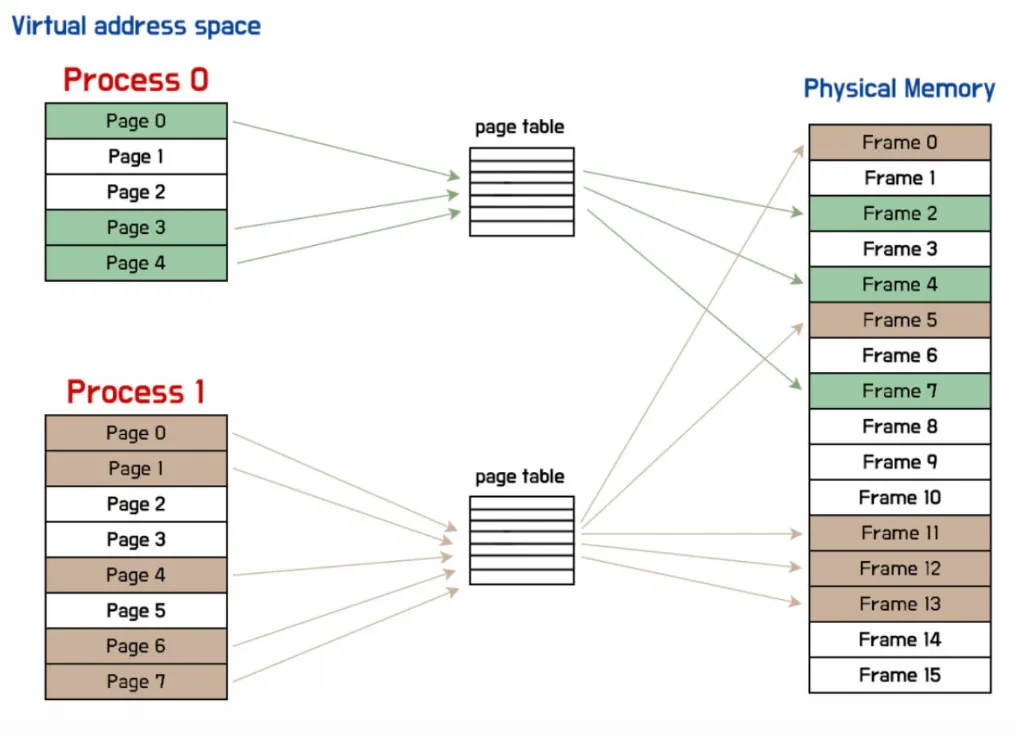
Page Faults
Valid bit
- on(1): page table에 virtual page number와 일치하는 physical page number 정보 존재
- off(0): page 정보가 disk에만 존재 → OS가 담당
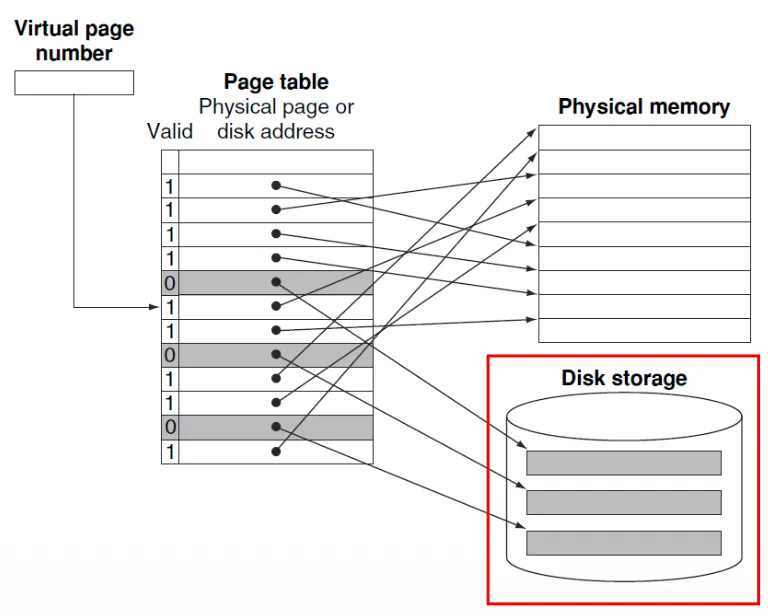
- 모든 페이지가 사용중이면 LRU에 따라 page 정보 교체
Reference bit(use bit)
- 가장 최근에 사용되었는가를 찾는 용도
- 1: 현재 접근되고 있음 → OS에 의해 주기적으로 0으로 초기화
- 0: 최근에 사용되지 않음
Disk writes는 너무 오래 걸림
- Write through는 비실용적 → write back 사용
- Dirty bit → 페이지가 쓰여질 때 사용
Making Address Translation Fast using TLB
Page table은 main memory에 저장됨
- 프로그램에 의한 모든 메모리 접근이 최소 2배 시간이 걸릴 수 있음
- physical address를 얻기 위한 접근
- 실제 data로의 접근
Translation-lookaside buffer(TLB)
- Page table의 Cache 버전
- page table에 대한 접근을 피하기 위해 recently used address mappings를 유지하는 cache

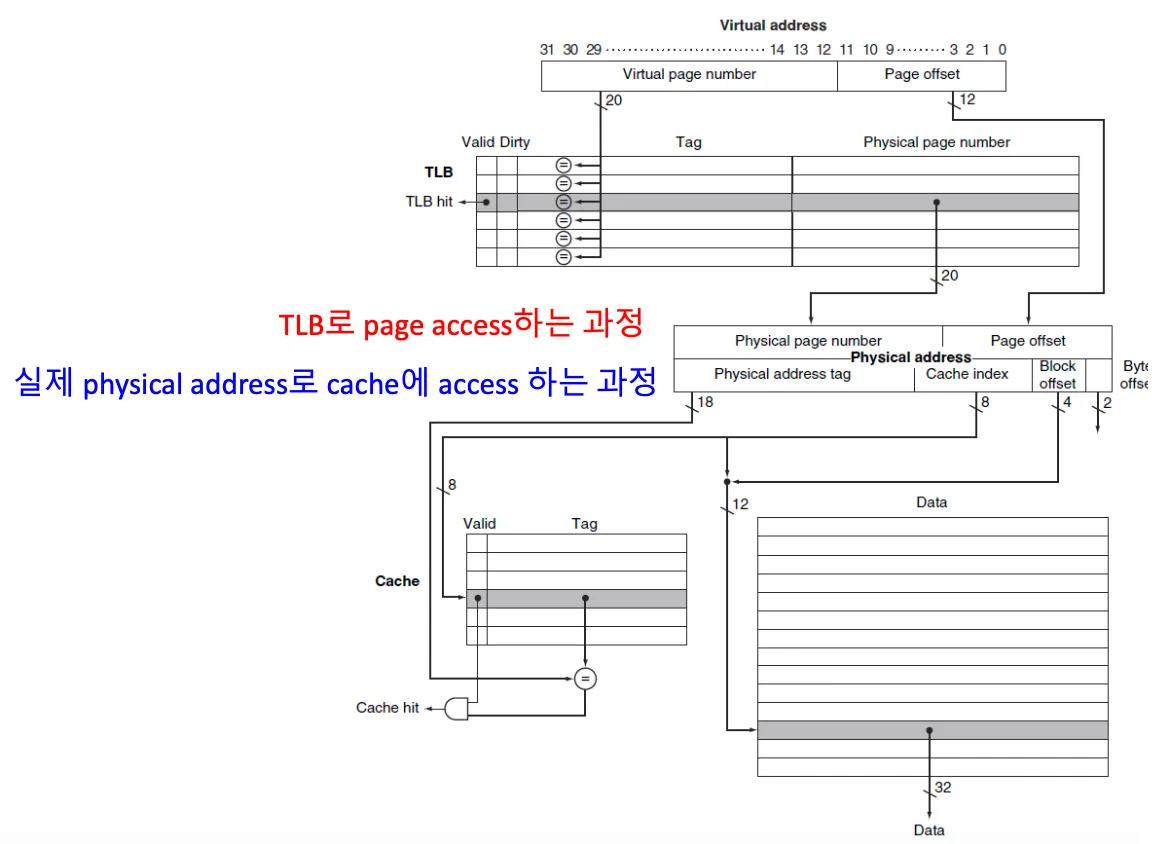

Handling TLB Miss and Page Faults
TLB miss
- TLB에 없고, main memory에 있는 경우 → 언젠가 불리긴 했는데, 최근에 안쓰임
Page Fault
- TLB가 가리키는 page가 main memory에 없는 경우 → 한 번도 불린 적이 없거나, 정말 옛날에 불렸거나
- virtual address를 통해 page table에서 디스크를 참조하는 page의 location을 탐색
- 교체할 physical page를 선택 → dirty bit인 경우 disk에 수정된 값을 우선 저장
- 선택된 Physical page에 디스크로부터 참조된 page를 가져옴
- 인스트럭션을 restartable하게 함 → address들을 업데이트하고 Ref: 1, Valid: 1, Dirty: 0
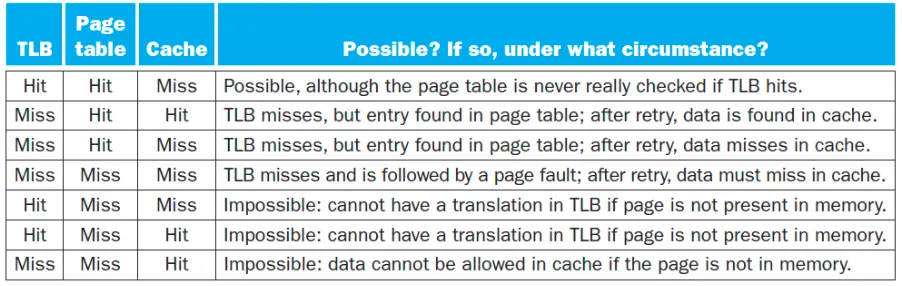
→ Miss, Miss, Miss: Page Fault
→ 저장용량: TLB < Cache < Page Table(=Main Memory) < Disk
728x90
반응형
'Computer Science > Computer Architecture' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컴퓨터구조] Lecture 19: Memory Hierarchy - Part3 (0) | 2026.02.12 |
|---|---|
| [컴퓨터구조] Lecture 17: Memory Hierarchy - Part1 (0) | 2026.02.12 |
| [컴퓨터구조] Lecture 15: The Processor - Part4 (0) | 2026.02.12 |
| [컴퓨터구조] Lecture 14: The Processor - Part3 (0) | 2026.02.12 |
| [컴퓨터구조] Lecture 13: The Processor - Part2 (0) | 2026.02.12 |