728x90
반응형
경희대학교 김정욱 교수님의 컴퓨터구조 강의를 기반으로 정리한 글입니다.
Pipeline Hazards
- Advantages of the Pipelining: Speed up → Improved performance
- Structure hazards
- Data hazards
- Control hazards
Structure Hazards
- 자원 충돌로 인해 발생
- 하드웨어가 같은 clock cycle 내에서 우리가 원하는 인스트럭션의 조합을 실행할 수 없는 문제
- CC4에서 인스트럭션과 데이터가 같은 메모리에 저장된 경우 → fetch, memory 단계가 같은 clock cycle에 겹치면, 같은 메모리에 동시에 접근하여 충돌 발생

Solution1: Stall(한 사이클 중지)

→ 하지만 2번 인스트럭션과 다시 겹침 → 3번씩 쉬어야 함
Solution2: 인스트럭션 메모리와 데이터 메모리를 나누기
Data Hazards
- 이전 인스트럭션의 WB이 반영되기 전에 WB에서 반영될 예정인 레지스터를 포함한 다음 인스트럭션의 EX가 실행되는 경우
- Pipeline 구조에서 R-format의 rd값이 다음 명령어의 rs 또는 rt에 위치할 때 문제 발생
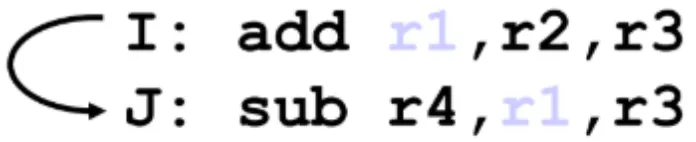
Example 1
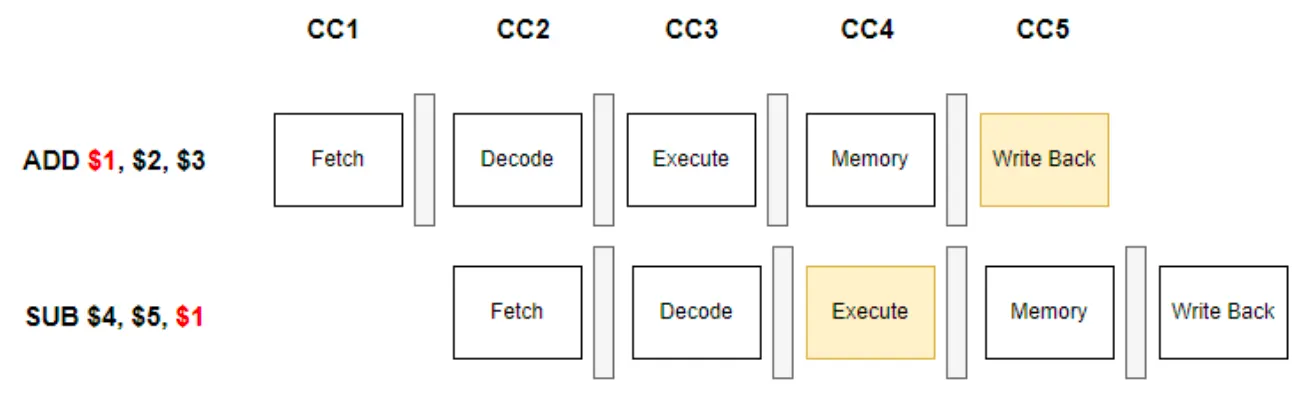
Naive Solution 1: Stall

→ but, 두 번의 clock cycle을 내다버림
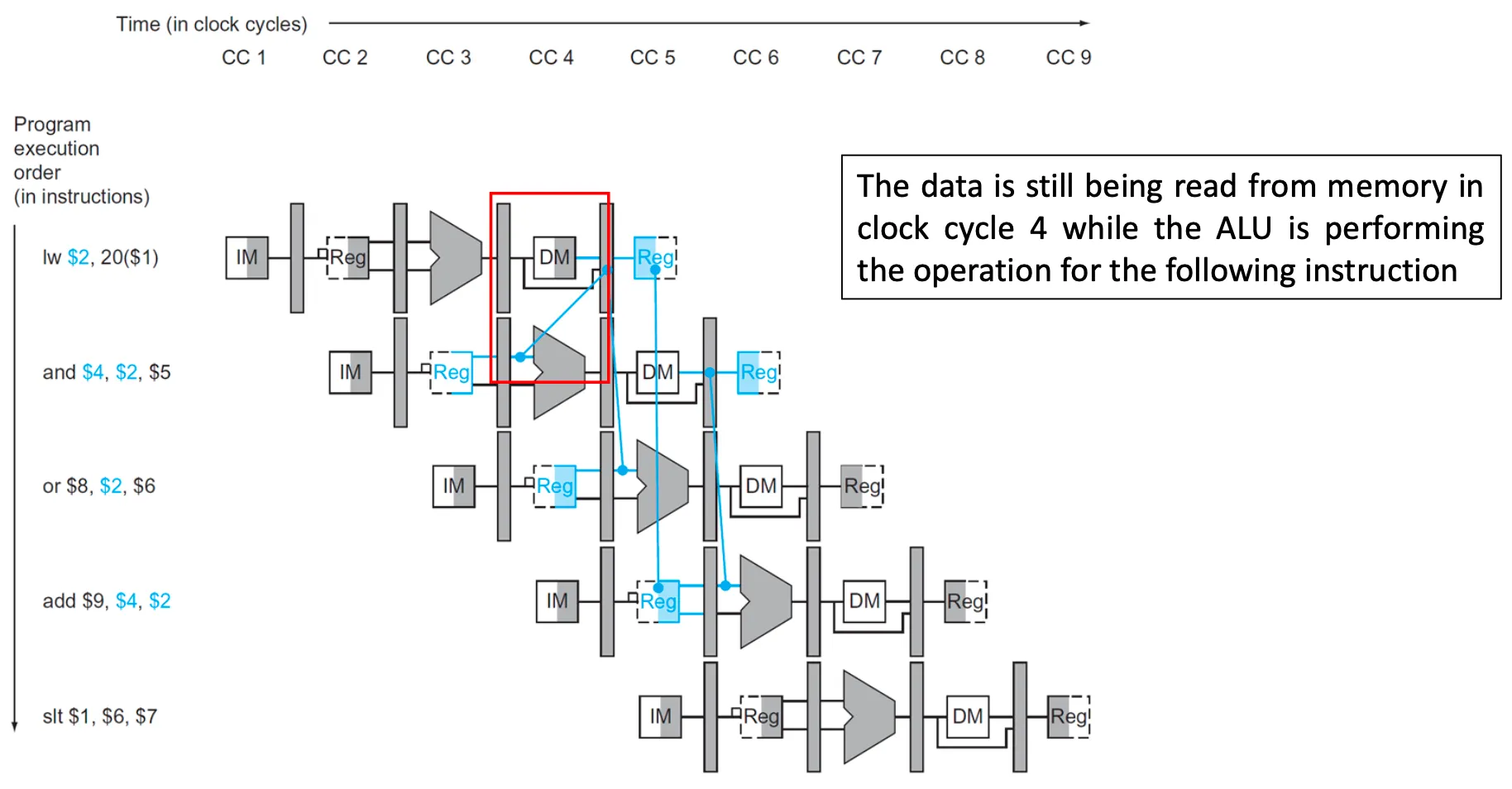
Primary solution: Forwarding or Bypassing
- 쉬는게 아니라 EX 단계에서 나온 WB 예정 값을 미리 다음 인스트럭션으로 넘겨줌

→ 넘겨주고 나면 나머지 단계는 정상적으로 수행

Load-use data hazard
- lw 인스트럭션 다음에 바로 사용되는 경우, 메모리에 접근해야하기 때문에 한 스테이지 쉬어야 함
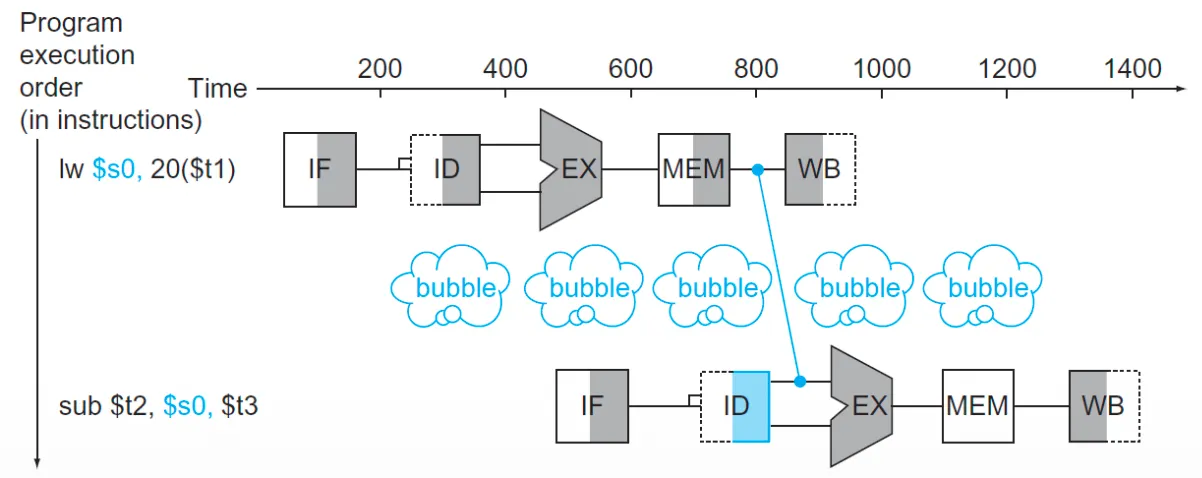
Solution: Reordering to avoid pipeline stalls

- 인스트럭션 순서를 적절히 배치 → 관련 없는 다른 인스트럭션 수행 → 시간 벌어줌
Review

→ 이후 2개의 인스트럭션까지 영향을 미침
Notation of data hazard conditions
- Format: AA/BB.RegisterRd = CC/DD.RegisterRs or CC/DD.RegisterRt
- ex. ID/EX.RegisterRs: ID/EX에서 발견되는 Rs 번호
- 1a. EX/MEM.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRs → EX/MEM 단계의 rd가 다음 인스트럭션의 ID/EX 단계의 rs와 같음 : 1a hazard
- 1b. EX/MEM.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRt → EX/MEM 단계의 rd가 다음 인스트럭션의 ID/EX 단계의 rt와 같음 : 1b hazard
- 2a. MEM/WB.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRs → MEM/WB 단계의 rd가 다음 인스트럭션의 ID/EX 단계의 rs와 같음 : 2a hazard
- 2b. MEM/WB.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRt → MEM/WB 단계의 rd가 다음 인스트럭션의 ID/EX 단계의 rt와 같음 : 2b hazard
- 현재 인스트럭션이 읽는(Rs 또는 Rt) register 번호와 이전 인스트럭션이 write하는(Rd) register 번호와 같은지 체크 → 만족하면 바로 forwarding 수행
Forwarding

Detecting data hazards
EX hazard
// R-format에서 이전 인스트럭션의 EX/MEM의 rd가
// 현재 인스트럭션의 ID/EX의 rs 또는 rt와 같으면 포워딩
// 1a hazard
if (EX/MEM.RegWrite // R-format 또는 lw
and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd != 0) // Rd가 유효하다 -> lw가 아님
and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd == ID/EX.RegisterRs)) ForwardA = 10
// 1b hazard
if (EX/MEM.RegWrite // R-format 또는 lw
and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd != 0) // Rd가 유효하다 -> lw가 아님
and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd == ID/EX.RegisterRt)) ForwardB = 10
MEM hazard
// 2a hazard
if (MEM/WB.Regwrite
and (MEM/WB.RegisterRd != O)
and (MEM/WB.RegisterRd == ID/EX.RegisterRs)) ForwardA = 01
// 2b hazard
if (MEM/WB.Regwrite
and (MEM/WB.RegisterRd != 0)
and (MEM/WB.RegisterRd == ID/EX.RegisterRt)) ForwardB = 01
Additional case

- MEM hazard를 고려할 때 EX hazard가 연속인 상황도 고려해야 함
//2a hazard
if (MEM/WB.RegWrite
and (MEM/WB.RegisterRd != 0)
and not(EX/MEM.RegWrite and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd != 0)
and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd == ID/EX.RegisterRs))
and (MEM/WB.RegisterRd == ID/EX.RegisterRs)) ForwardA = 01;
//2b hazard
if (MEM/WB.RegWrite
and (MEM/WB.RegisterRd != 0)
and not(EX/MEM.RegWrite and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd != 0)
and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd == ID/EX.RegisterRt))
and (MEM/WB.RegisterRd == ID/EX.RegisterRt)) ForwardB = 01;

Load-use data hazards
- lw의 rt를 다음 인스트럭션의 rs 또는 rt와 같은 경우 → 최대한 빨리 stall
if (ID/EX.MemRead and // ID/EX의 MemRead를 읽고 있는 상태 -> 현재 인스트럭션이 lw 다음에 수행
((ID/EX.RegisterRt == IF/ID.RegisterRs) or
(ID/EX.RegisterRt = IF/ID.RegisterRt))) // lw의 rt가 현재 R-format의 rs 또는 rt에 대응되는지 확인
stall the pipeline;
- stall 하는 방법 → Insert nop(no operation)
- nop: 상태를 바꾸는 연산을 진행하지 않는 명령어

Pipeline control overview

728x90
반응형
'Computer Science > Computer Architecture' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컴퓨터구조] Lecture 18: Memory Hierarchy - Part2 (0) | 2026.02.12 |
|---|---|
| [컴퓨터구조] Lecture 17: Memory Hierarchy - Part1 (0) | 2026.02.12 |
| [컴퓨터구조] Lecture 14: The Processor - Part3 (0) | 2026.02.12 |
| [컴퓨터구조] Lecture 13: The Processor - Part2 (0) | 2026.02.12 |
| [컴퓨터구조] Lecture 12: The Processor - Part1 (0) | 2026.02.12 |