728x90
반응형
경희대학교 김정욱 교수님의 컴퓨터구조 강의를 기반으로 정리한 글입니다.
Control Hazards
- Branch 수행할 때 발생 가능(ex. beq, bne)

Five Solution Candidates
1. Stall until branch direction is clear
- pipelining의 의미가 사라짐
2. Predict branch not taken
- PC+4가 이미 계산되어 있으니 실행하자
- 평균 47% MIPS branch가 not taken
- 만약 taken인 경우 → PC+4 인스트럭션은 버려짐
3. Predict branch taken
- branch address의 인스트럭션을 선택
- 평균 53% 맞음
- 만약 not taken인 경우 → 버려짐
4. Execute both paths
- CPU 2개를 사용해 not taken, taken 모두 실행
- 돈이 많아야 함
5. Delay of branches

- reordering
- branch의 결과가 나올 때까지(3cycle) branch 결과와 관계 없는 인스트럭션 수행
Example


- 인스트럭션 2개 낭비 → 한 인스트럭션이라도 더 일찍 발견하고 싶음
- ID 단계에서 이미 값들은 아니까 같은지 보는 Comparator가 있으면 되겠다
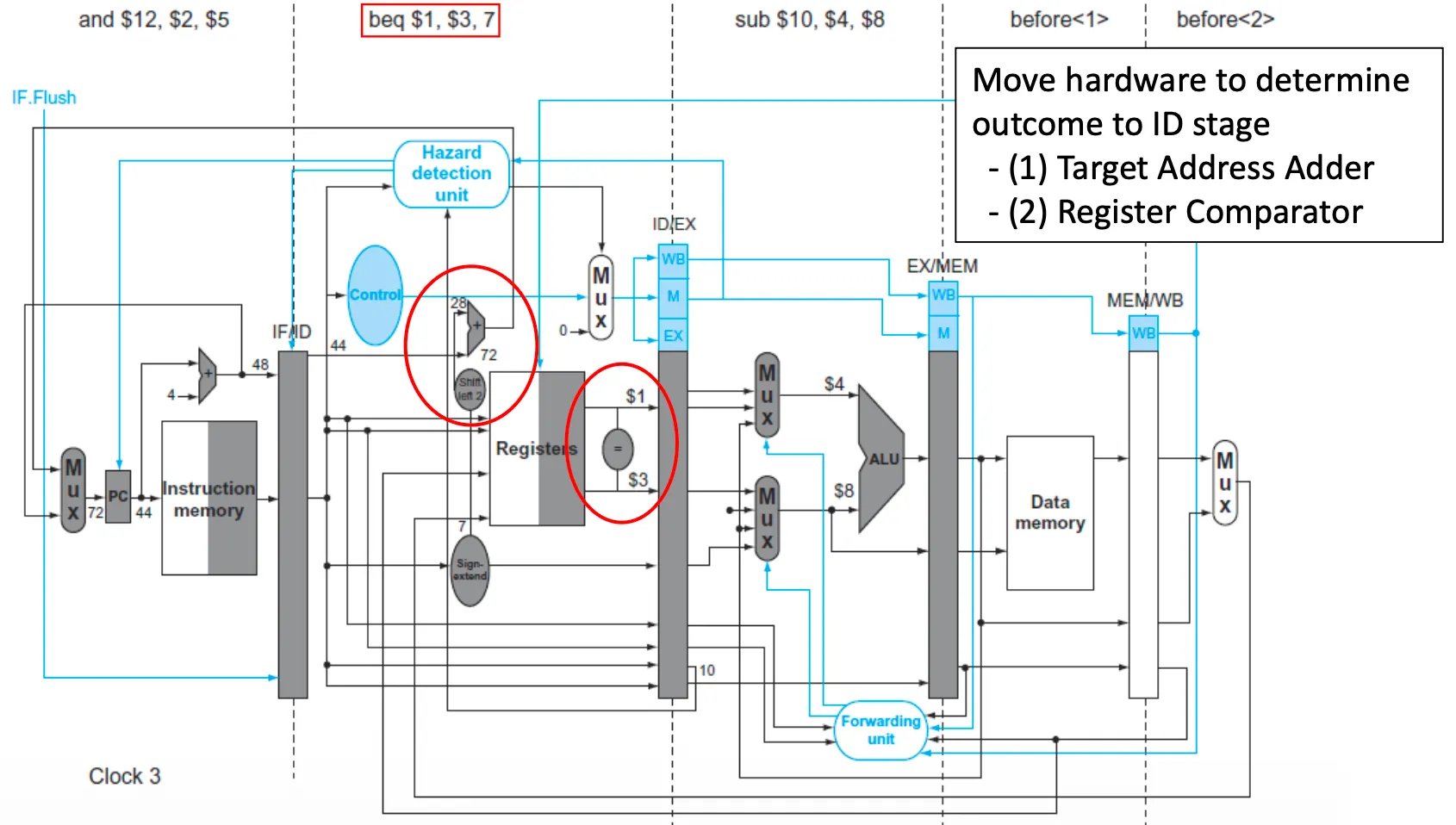
- 만약 $1, $3이 같으면

- bubble(nop: no operation)을 하고 branch한 목적지 인스트럭션을 fetch
Dynamic Branch Prediction
- Branch history table을 보고 branch 할지 말지 결정
- branch prediction buffer는 메모리가 작다(1 or 2 bits)
Branch prediction buffer(1-bit)
- 이전 결과를 저장: branch taken(1), branch not taken(0)
- Nested Loop 구조에서
- Inner loop가 계속 branch taken(1) 되다가 어느 순간 빠져나올 때, 한 번의 miss → branch not taken(0)으로 변경
- 하지만 outer loop가 실행되어 inner loop가 다시 실행되면 branch taken(1) 해야 되는데 branch not taken(0)으로 되어 있어서 추가적인 miss 발생

Branch prediction buffer(2-bits)
- branch prediction이 연속으로 2번 틀려야 상태 변경

1-bit predictor vs. 2-bits predictor

Exception
Exception
- undefined 인스트럭션이 실행될 때, arithmetic overflow가 발생할 때
Interrupt(in MIPS)
- 프로세서 외부에서 발생하는 예외
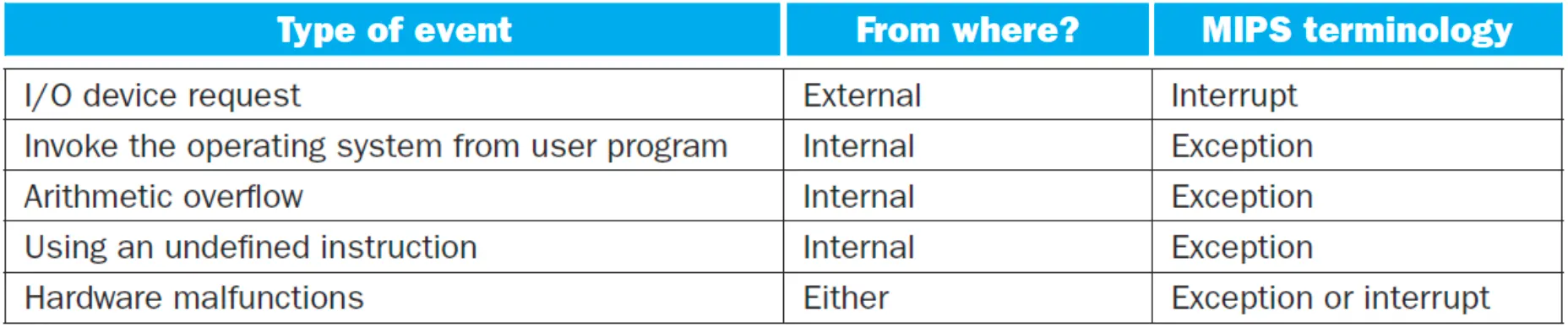
Handling Exceptions in MIPS
Procedure
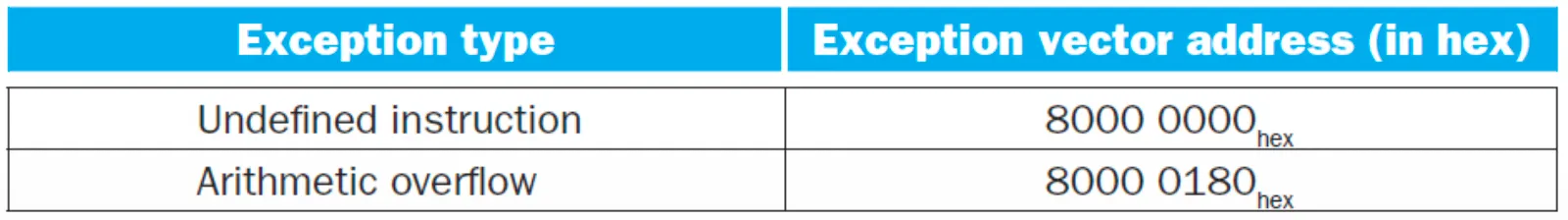
- 문제가 생긴 인스트럭션의 (PC+4)를 EPC(Exception Program Counter, 32-bits)에 저장
- Cause Register(32-bits)에 예외 이유 저장 → 10: undefined instruction, 12: arithmetic overflow
- Jump to handler
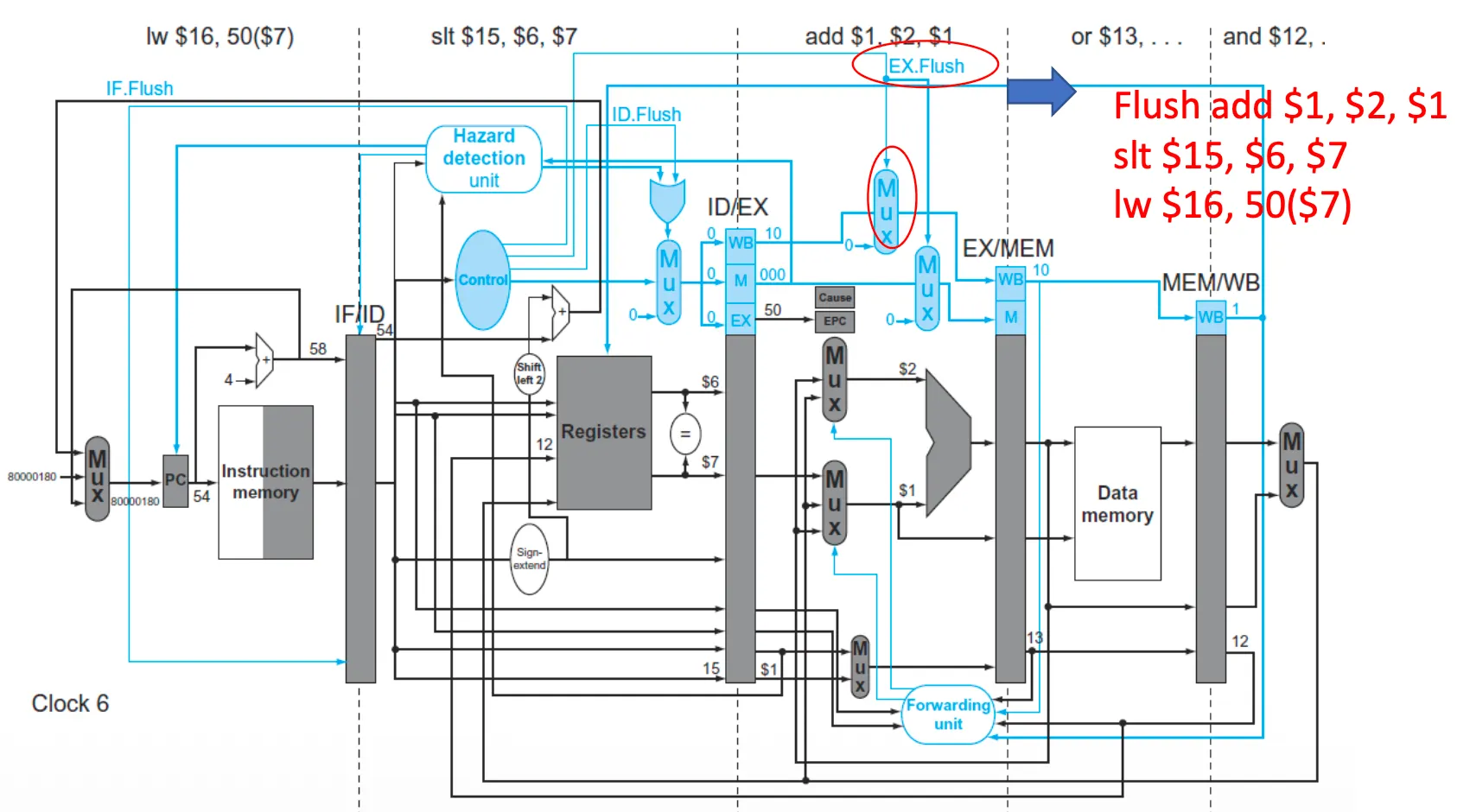
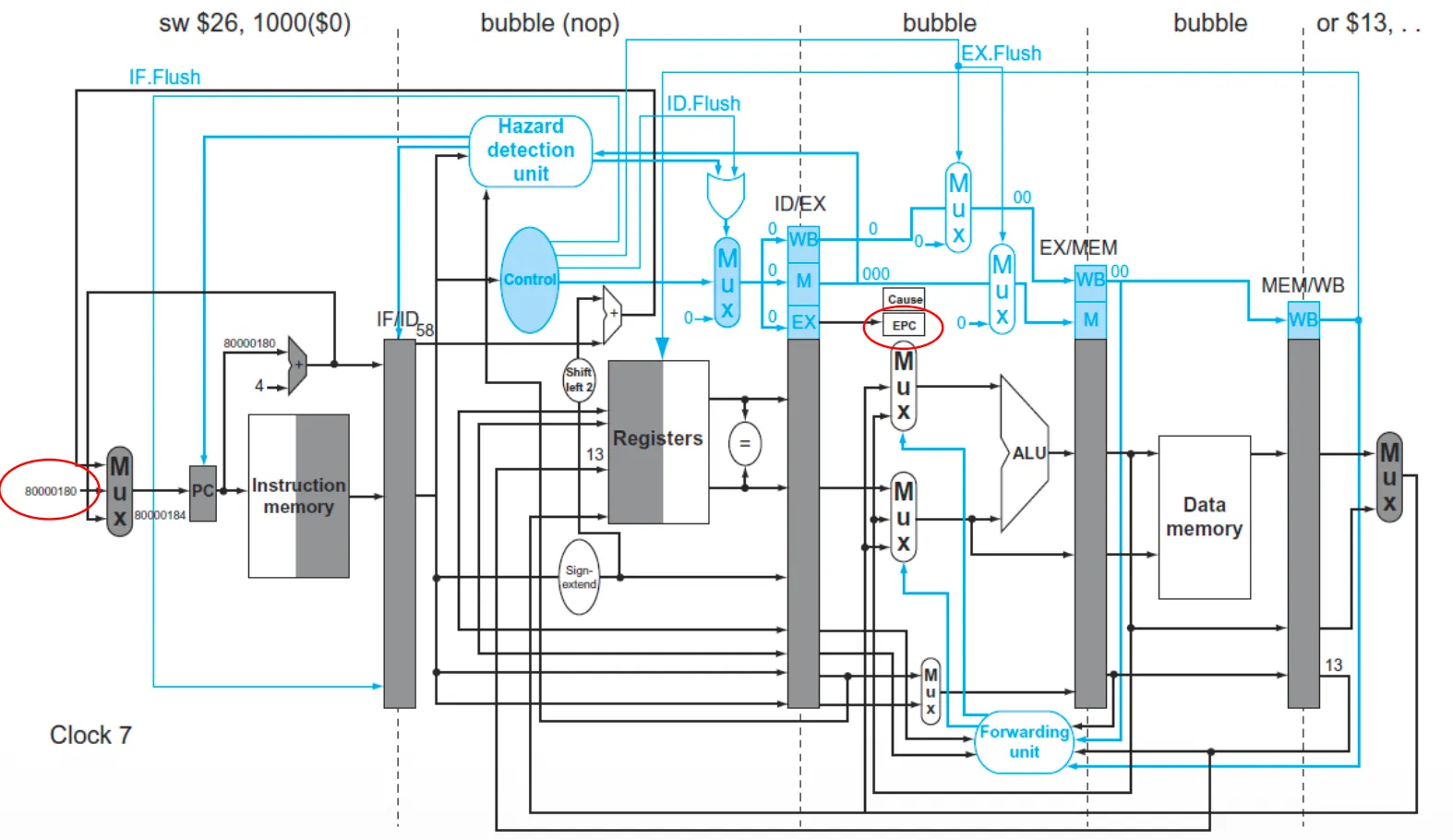
Handling Exceptions in Pipeline

- EX 단계(ALU)에서 add 인스트럭션이 오버플로우 발생
- 오버플로우 값이 $s1에 저장되는 것을 막음
- 이전 인스트럭션들을 완료
- add 다음 인스트럭션들을 비움(flush) → EX.Flush
- EPC와 Cause Register 설정
- overflow handler(8000 0180)으로 jump


- CC6 → 44: WB, 48: MEM, 4C: EX, 50: ID, 54: IF
- EX 단계에서 add 과정 중 overflow 발생 → PC에 8000 0180 저장
- CC7에서 add 포함 이후 인스트럭션 flush
- exception code의 첫 번째 인스트럭션 fetch
- 50(예외 발생 다음 인스트럭션 주소) EPC에 저장
728x90
반응형